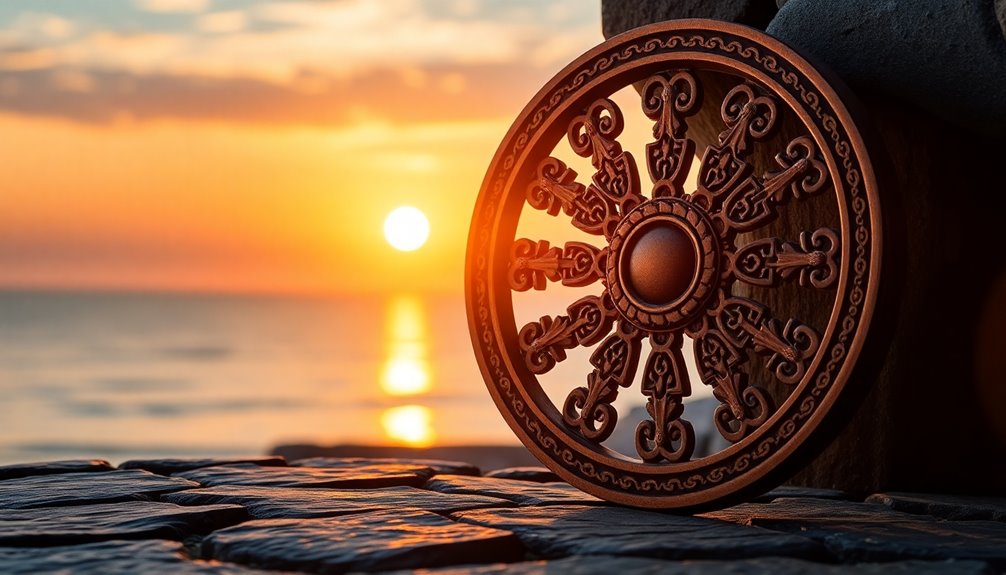
The Wheel of Dharma is a profound symbol in Buddhism, representing the essence of Buddha's teachings and the journey toward enlightenment. With its eight spokes, it embodies the Noble Eightfold Path, guiding you to spiritual awakening. The wheel's circle symbolizes completeness and unity, while the hub signifies discipline essential for practice. First seen in ancient Indian art, this emblem connects to the beginning of Buddha's teachings at Sarnath. Significant for promoting peace and ethics, the Wheel of Dharma influences both spiritual practice and cultural expressions today. Keep exploring, and you'll uncover even more layers of its remarkable significance.
Key Takeaways
- The Wheel of Dharma symbolizes the Buddha's teachings and the path to enlightenment, representing liberation from suffering.
- Its eight spokes correspond to the Noble Eightfold Path, guiding practitioners toward spiritual awakening and ethical living.
- The circular shape signifies the perfection and completeness of Buddhist doctrine, emphasizing unity and harmony in practice.
- Historically, the wheel gained prominence through Emperor Ashoka, who adorned pillars with Dharma wheels, spreading its significance.
- Today, it transcends Buddhism, symbolizing peace and unity across cultures, celebrated during rituals like Dharmachakra Day.
Definition and Origin of the Wheel
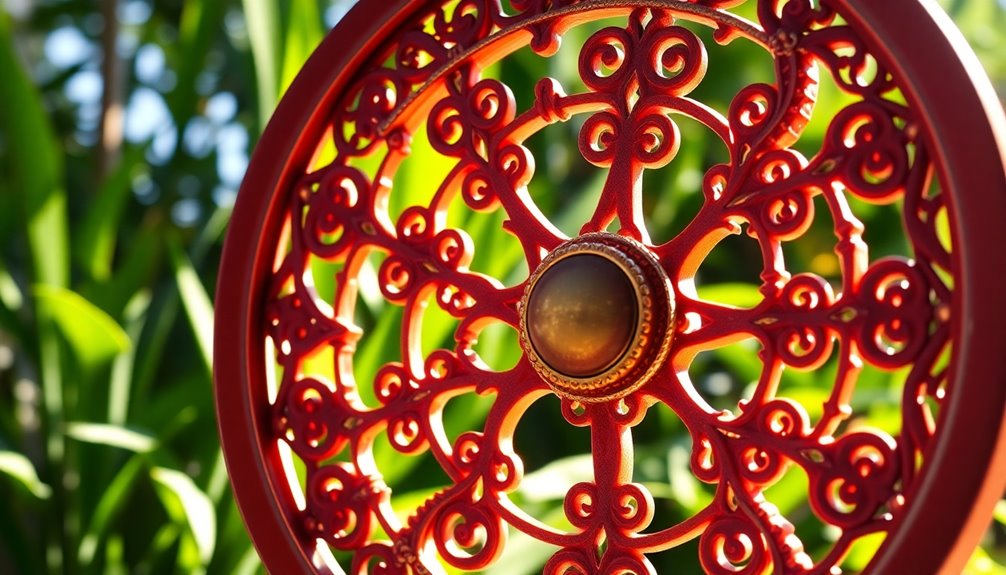

The Wheel of Dharma, also known as the Dharmachakra, serves as a central symbol in Buddhism, embodying the essence of the Buddha's teachings and the journey toward enlightenment.
This sacred symbol translates to the "Wheel of Dharma" or "Wheel of Law," representing the core principles of Buddhism and the path to liberation from suffering.
Historically, the wheel first appeared in Indian artwork before Emperor Ashoka's reign, with his pillars prominently featuring it between 304 and 232 BC.
Legend has it that the wheel began turning when the Buddha delivered his first sermon in Sarnath, Uttar Pradesh, sharing the profound teachings that guide practitioners toward enlightenment. The wheel's structure, composed of the hub, spokes, and rim, serves to illustrate the interconnectedness of discipline and the Noble Eightfold Path in achieving spiritual progress.
The artistic representations of the Wheel have varied, often depicted with multiple spokes, such as the 24 spokes in Ashoka Chakras.
Its presence extends beyond Buddhism, appearing in Hinduism and Jainism, showing its universal significance.
Symbolism of the Wheel Components
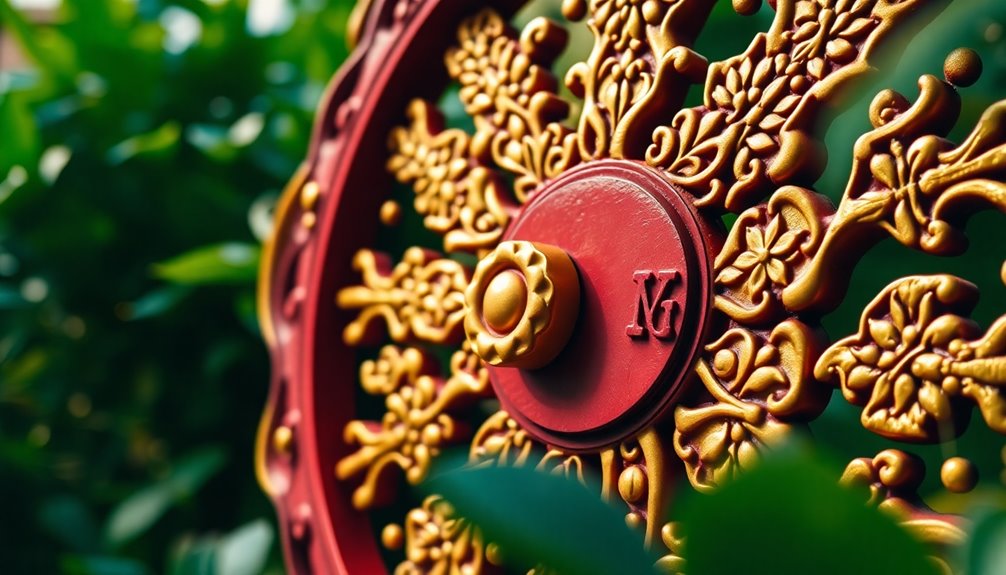

When you look at the Wheel of Dharma, each component offers deep symbolism that enriches your understanding of Buddhist teachings. The circle itself represents the perfection of the dharma, signifying the completeness and unity of the Buddha's doctrine. It embodies the cycle of life and the path to enlightenment, emphasizing the eternal nature of these teachings.
The eight spokes of the wheel correspond to the Noble Eightfold Path. Each spoke represents an essential aspect: Right View, Right Resolve, Right Speech, Right Conduct, Right Livelihood, Right Effort, Right Mindfulness, and Right Samadhi. These spokes guide you toward spiritual awakening and liberation while reflecting the balance and harmony necessary for personal growth. Mindfulness, compassion, and ethical living are integral to each aspect of the path, encouraging practitioners to embody these values in daily life.
At the center, the hub symbolizes discipline, which is vital for progress along the Buddhist path. It holds everything together, signifying unity and cohesion in your practice.
Often depicted with a hand, it represents the Buddha "turning the wheel of dharma," emphasizing the importance of discipline in your journey. Additional elements, like deer and lotus flowers, enrich the symbolism, reminding you of key teachings and events in Buddhism.
Understanding the Noble Eightfold Path
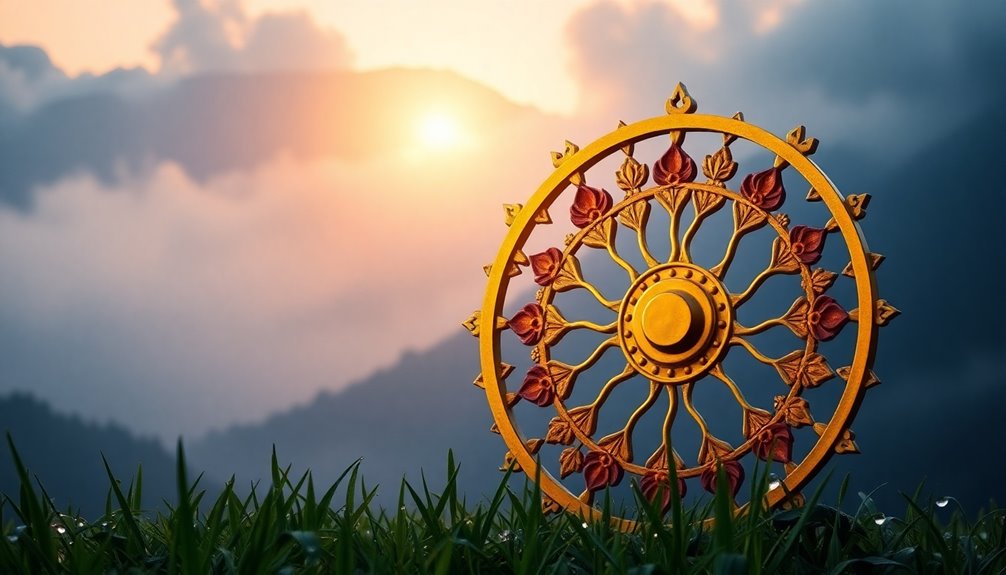

Embracing the Noble Eightfold Path offers a transformative journey toward spiritual awakening and liberation. This path consists of eight interconnected components that guide your actions and thoughts.
First, Right View helps you grasp the Four Noble Truths, karma, and rebirth. Understanding these concepts lays the foundation for your journey.
Next, Right Resolve encourages non-violence and the intention to cultivate compassion. The teachings of the Dharma Wheel emphasize understanding the nature of suffering and its cessation.
Right Speech promotes truthful and kind communication, while Right Action advocates ethical conduct, urging you to avoid harm to others.
Right Livelihood emphasizes earning a living that doesn't cause suffering, aligning your work with your values.
The Noble Eightfold Path also categorizes these components into three sections: Wisdom (Paññā), Ethics (Sīla), and Concentration (Samādhi). Each category enhances your overall growth and development.
Practicing the path simultaneously fosters a holistic approach, cultivating skillful actions and mindfulness in your daily life.
Historical Importance of the Wheel

Throughout history, the Wheel of Dharma has held profound significance in Buddhism and Indian culture. You can trace its origins back to ancient Indian traditions, where wheels symbolized motion and change. The Buddha adopted this motif to represent his teachings, initiating the metaphorical "wheel" of law and order.
The Dharmachakra first appeared in ancient Buddhist texts, notably in the Pali Canon, and it evolved into a prominent visual symbol in Buddhist art and architecture.
Emperor Ashoka played a crucial role in popularizing this symbol. He built pillars adorned with Dharma wheels between 304 and 232 BC, promoting the practice of Buddhism through edicts encouraging non-coercive adherence. His iconic Ashoka Chakras, featuring twenty-four spokes, became a significant part of Buddhist symbolism. This twenty-four spokes design reflects the importance of the teachings and the path to enlightenment.
Before Ashoka, the Dharmachakra already appeared in Indian artwork, often symbolizing not only the Buddha's teachings but also the Buddha himself.
Today, the Wheel continues to represent peace and unity, transcending its original context. Its imagery remains influential, manifesting in modern art, sculptures, and rituals like Dharmachakra Day, reminding you of its enduring legacy.
Cultural Representations and Artistry

The Wheel of Dharma's significance extends well beyond its historical roots, manifesting in diverse cultural representations and artistic expressions across various regions. You'll find that the Dharmachakra symbolizes peace and unity, permeating cultures beyond Buddhism itself. As it traveled to countries like Tibet, China, and Japan, local cultures infused the symbol with unique artistic elements while preserving its core meaning.
In Buddhist art, the Dharmachakra has evolved over centuries, appearing in temple murals, manuscripts, and sculptures. You'll notice variations in artistic styles, from simple forms to intricate designs, often featuring a hand at the center, symbolizing the Buddha's teachings. The wheel's design reflects the importance of the Noble Eightfold Path, which guides practitioners toward enlightenment.
The wheel graces architecture as well, prominently featured in stupas and monasteries, marking the spread of Buddha's teachings. During rituals, the Dharmachakra symbolizes the Buddha's first sermon at Sarnath, commemorated on Dharmachakra Day.
Engaging with the wheel through meditation helps internalize these teachings. As you explore its rich cultural tapestry, you'll uncover how the hub and rim of the wheel signify moral discipline and concentration, essential for your spiritual journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Is the Dharma Wheel Used in Meditation Practices?
In meditation practices, you use the Dharma Wheel as a focal point to enhance your concentration.
By visualizing its components, you reflect on the Buddha's teachings and your spiritual journey.
Spinning prayer wheels engages your body, speech, and mind, helping to settle your thoughts.
This practice cultivates mindfulness and aids in karmic purification, allowing you to deepen your understanding of the path to enlightenment while connecting with the essence of Buddhism.
Can the Dharma Wheel Be Found in Non-Buddhist Cultures?
Yes, you can find the Dharma Wheel in various non-Buddhist cultures.
It has been adopted in Hinduism, where it symbolizes order and law, often associated with the god Vishnu.
Additionally, Jainism incorporates the wheel as a representation of the spiritual path.
As you explore these traditions, you'll see how the wheel's meaning evolves, yet it consistently reflects themes of spirituality, balance, and the cyclical nature of life across different cultures.
What Are Common Misconceptions About the Dharma Wheel?
You might think the Dharma Wheel is exclusive to Buddhism, but it appears in Hinduism and Jainism too.
Many believe it has to have eight spokes, yet the number can vary, representing different teachings. The wheel isn't just a static symbol; it represents dynamic spiritual progress.
Also, it's not solely about the Noble Eightfold Path; it can symbolize the Four Noble Truths and other key concepts in Buddhism.
How Does the Dharma Wheel Relate to Modern Mindfulness Practices?
The Dharma Wheel relates to modern mindfulness practices by emphasizing present-moment awareness and reflection.
You can integrate its teachings into your daily life, fostering ethical thoughts and actions.
By practicing meditation techniques like Shamatha and Vipashana, you're enhancing your understanding of reality.
The Wheel encourages you to make mindful choices, helping you manage stress and develop resilience, ultimately leading to a more balanced and harmonious life amidst today's challenges.
Are There Variations of the Dharma Wheel in Different Buddhist Traditions?
Yes, there are several variations of the Dharma Wheel across different Buddhist traditions.
For instance, the Tibetan Wheel of Life illustrates the cycle of samsara, while Kadampa temples often depict the wheel flanked by deer.
Each tradition emphasizes unique aspects, like the number of spokes representing different teachings.
Regardless of the form, these variations maintain the core principles of Buddha's teachings, reflecting the richness and diversity within Buddhist practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Wheel of Dharma isn't just a symbol; it's a profound representation of life's journey and spiritual growth. By understanding its components and the Noble Eightfold Path, you gain insight into the teachings of Buddhism and the importance of balance in your life. As you explore its historical significance and cultural representations, you'll appreciate its deep-rooted impact on countless lives. Embrace the wisdom of the Wheel, and let it guide you on your own path to enlightenment.