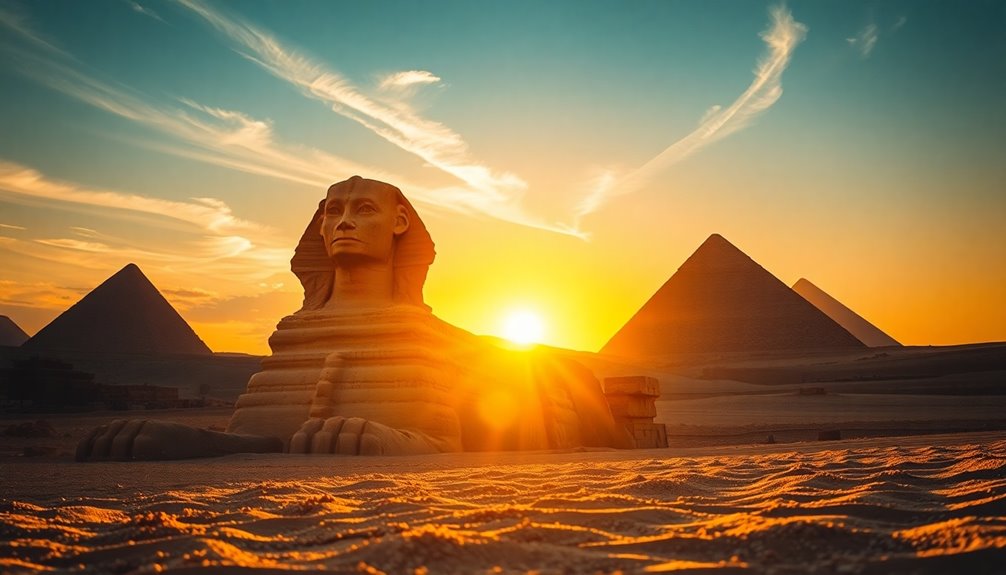
The age of the Sphinx is a hot topic that raises questions about Egypt's historical timeline. While it's traditionally dated to around 2500 B.C., some evidence suggests it might be thousands of years older, dating back to 5000 B.C. or even earlier. Geological studies reveal erosion patterns that imply severe weathering from wetter climates, not just wind and sand. Researchers like Dr. Robert Schoch argue for an ancient origin that challenges what we thought we knew about early civilizations. If you're curious about the implications of these findings, there's plenty more to uncover about this fascinating debate.
Key Takeaways
- The Great Sphinx may date back to 5000 B.C. or earlier, challenging traditional timelines centered around Pharaoh Khafre's reign around 2500 B.C.
- Geological studies indicate significant water erosion patterns, suggesting the Sphinx experienced wetter conditions over 12,000 years ago, conflicting with current arid climate assumptions.
- Dr. Robert Schoch's research supports the idea of an ancient Sphinx predating the Old Kingdom, based on erosion patterns inconsistent with established wind and sand theories.
- The existence of advanced structures like Gobekli Tepe raises questions about the capabilities of prehistoric cultures, potentially indicating earlier sophisticated civilizations.
- Future research integrating advanced geological studies and skepticism can provide deeper insights into the Sphinx's age and the broader context of ancient Egyptian history.
Historical Context of the Sphinx

The Great Sphinx of Giza stands as a monumental tribute to ancient Egyptian civilization, capturing the imagination of historians and archaeologists alike. While traditional beliefs place its construction around 2500 B.C. during Pharaoh Khafre's reign, evidence suggests the Sphinx might be much older, potentially dating back to 5000 B.C. or earlier. This raises intriguing questions about the age of the Sphinx and its historical context.
Notably, pioneers like Sir Flinders Petrie argued for its greater age than the Old Kingdom, while Sir Gaston Maspero suggested Khafre may have unearthed it rather than built it. This debate connects deeply with oral traditions that hint at the Sphinx's existence long before Khafre's time.
Such traditions, alongside findings from an inventory stela, point to a more ancient timeline than conventionally accepted.
The ongoing discussions about the Sphinx challenge our understanding of ancient Egyptian history and the environmental conditions at that time. With theories linking its age to possible water erosion, you can't help but wonder if the Sphinx holds secrets to a complex history waiting to be uncovered.
Geological Insights and Erosion

Questions about the Sphinx's age lead us to examine geological evidence that reveals the monument's fascinating erosion patterns. Geological studies show significant water erosion inconsistent with today's arid climate, suggesting the Sphinx was constructed during a much wetter period over 12,000 years ago. The erosion features align with water exposure rather than just wind and sand, raising questions about the timeline of the Old Kingdom.
The Sphinx's position in the Nile floodplain means historical water table fluctuations could have influenced its erosion and preservation. Here's a deeper look at the factors affecting the Sphinx's condition:
| Factor | Impact on Erosion |
|---|---|
| Water Erosion | Indicates wetter climate periods |
| Nile Floods | Historically washed away salt deposits |
| Groundwater Dynamics | Increased levels due to urbanization |
| Historical Flood Cycles | Maintained structural integrity |
| Aswan Dam Construction | Disrupted natural flooding cycles |
Understanding these erosion patterns offers critical insights into the Sphinx's history and challenges the conventional narrative of its age. By examining these geological aspects, you can appreciate the monument's resilience against time.
Dr. Robert Schoch's Findings

Challenging established timelines, Dr. Robert M. Schoch's groundbreaking research on the Sphinx enclosure reveals compelling evidence that the structure may be much older than previously thought.
His geological studies indicate that the erosion caused by significant rainfall, rather than the traditional wind and sand erosion, suggests a date as far back as 10,000 BC. This aligns with findings from other ancient sites, hinting at an advanced culture or even a lost civilization.
Here are some key points from Schoch's findings:
- Subsurface weathering patterns support an ancient Sphinx predating the Old Kingdom.
- Erosion features correspond with environmental conditions not typical for Egypt today.
- Seismic studies reveal extraordinary geological changes beneath the Sphinx.
- Chronological alignment with Gobekli Tepe challenges the timeline of human development.
- Historical reevaluation of human civilization may be necessary based on these findings.
Implications of an Older Timeline

An older timeline for the Great Sphinx could considerably reshape our understanding of ancient civilizations. If the Sphinx dates back to as early as 5000 B.C., it challenges established timelines and suggests a more intricate prehistoric culture than we've previously recognized. Geological evidence of water erosion seen on the Sphinx aligns with a much wetter climate over 12,000 years ago, prompting a reevaluation of ancient Egypt's environmental conditions.
The implications of an older Sphinx extend far beyond Egypt. You might find that it raises questions about the technological and architectural capabilities of ancient civilizations, potentially indicating advanced knowledge and skills that we have yet to fully grasp. This discovery could even lead to a reassessment of other ancient structures worldwide, encouraging a broader investigation into human advancement.
Here's a quick look at the implications of this older timeline:
| Aspect | Implications |
|---|---|
| Dating of the Sphinx | Challenges established timelines |
| Erosion Patterns | Suggests a wetter climate |
| Architectural Skills | Indicates advanced knowledge |
| Historical Narratives | Calls for reevaluation |
| Global Structures | Inspires broader investigations |
Challenges to Conventional Beliefs

Frequently, conventional beliefs about the Great Sphinx face serious scrutiny as new evidence emerges. Many scholars now suggest that the Sphinx could be much older than previously thought, with some dating it back to 10,000 BC or earlier. This challenges the traditional timeline that places its construction around 2500 BC during Pharaoh Khafre's reign.
Dr. Robert Schoch's research highlights that erosion patterns on the Sphinx indicate water exposure, suggesting a wetter climate than Egyptologists believe. Furthermore, the existence of ancient structures like Gobekli Tepe raises questions about the sophistication of early human societies, prompting skepticism about established narratives.
Consider the following points:
- Geological studies imply the Sphinx's age could be thousands of years earlier.
- Oral traditions hint at its existence long before Khafre's time.
- Water erosion contradicts wind erosion theories.
- The potential suppression of alternative histories complicates the narrative.
- Discoveries of ancient structures challenge conventional timelines.
These pieces of evidence suggest that the Sphinx, buried in sand for millennia, may hold secrets that could reshape our understanding of ancient civilizations.
The ongoing debate emphasizes that skepticism would be wise when interpreting history.
Archaeological Perspectives and Criticism

You'll find that skepticism runs deep within the archaeological community regarding claims of an older Sphinx, as experts often interpret evidence in conflicting ways.
While some propose alternative theories about its origins, others dismiss these ideas, emphasizing the need for credible archaeological support.
This ongoing debate highlights the challenges and complexities that come with understanding the Sphinx's true age.
Skepticism in Archaeological Community
While some researchers champion the idea of an ancient Sphinx predating known Egyptian civilization, skepticism within the archaeological community remains strong. Critics argue that the geological evidence supporting water erosion is often misinterpreted or coincidental. Established scientific methods frequently lead to conflicting interpretations, creating a divide among those who advocate for the Sphinx's antiquity and those who adhere to traditional timelines.
Key points of skepticism include:
- Questionable interpretations of geological evidence related to erosion patterns.
- Dismissal of alternative theories, such as pre-dynastic construction or advanced ancient civilizations.
- Lack of concrete evidence for prehistoric builders of the Sphinx.
- Critique of sensational claims involving aliens or giants as unfounded.
- Challenges in archaeology, where new scientific advancements complicate established narratives.
This ongoing debate highlights the complexities within the archaeological field.
As you explore the Sphinx's age, it's vital to reflect that skepticism can play an important role in shaping our understanding of history.
Balancing new theories with established evidence might just lead to a more thorough view of Egypt's ancient past.
Conflicting Interpretations of Evidence
The debate surrounding the Sphinx's age is marked by conflicting interpretations of evidence, reflecting the deep divisions within archaeological perspectives. Proponents of an older Sphinx argue that geological evidence points to weathering processes inconsistent with established timelines. Critics, however, maintain that these interpretations are often coincidental or misrepresented, favoring the validity of the more widely accepted timeline.
| Proponents | Critics |
|---|---|
| Emphasize geological evidence | Highlight lack of direct support |
| Cite weathering processes | Defend established timelines |
| Explore ancient evidence | Promote skepticism of alternative theories |
As scholars debate the Sphinx's origins, they confront challenges in reconciling differing interpretations of ancient evidence. The absence of credible builders for the prehistoric Sphinx hypothesis raises further skepticism. While some suggest fantastical explanations like alien or giant builders, the scientific community largely dismisses these as unfounded. Continuous advancements in geology and archaeology provide new insights, yet they also underscore the complexities that arise from these conflicting interpretations. Ultimately, the quest for understanding the Sphinx's age remains a contentious and evolving discussion.
Alternative Theories and Speculations
Exploring alternative theories and speculations about the Sphinx's age reveals a landscape filled with intrigue and skepticism.
Some skeptics within the archaeological community argue that claims of an older Sphinx lack credible evidence and often rely on misinterpretations. This leads to the dismissal of outlandish theories involving alien or giant architects. Yet, established scientific methods yield conflicting interpretations, as both proponents and opponents present compelling evidence.
Key points to reflect on include:
- Colin Reader's hypothesis links the Sphinx's degradation to runoff, suggesting a connection to a Solar Cult.
- Critics question the absence of clear historical narratives regarding the proposed prehistoric builders.
- The ongoing debate reflects broader challenges within archaeology, where new technology could reshape our understanding.
- Many theories surrounding the Sphinx's construction are speculative and often lack rigorous validation.
- Advancements in research methodologies might provide fresh insights into the Sphinx's true age.
As you explore these alternative theories, remember that each perspective contributes to the complex story of the Sphinx, challenging our understanding of ancient Egypt's timeline and cultural heritage.
Environmental Factors and Weathering

Understanding the environmental factors at play is essential to grasping the weathering patterns of the Sphinx. Weathering in this iconic structure isn't just about running water; it's greatly influenced by temperature and humidity changes. Historical conditions, such as periods when the Sphinx was partially buried in sand, further complicate our understanding of its erosion.
The table below summarizes key environmental factors affecting the Sphinx:
| Factor | Impact on Weathering | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Causes rapid fluctuations | Affects the west wall |
| Humidity | Influences erosion rates | Changes over time |
| Groundwater | Alters structural integrity | Affected by urban development |
| Rainfall | Contributes to erosion | Minimal in the desert climate |
The west wall of the Sphinx endures intense sunlight, leading to differential weathering that can compromise its durability. Additionally, groundwater dynamics, impacted by the Aswan Dam, have disrupted natural cycles, further exacerbating erosion. Understanding these environmental factors is vital for comprehending the Sphinx's ongoing weathering process.
Future Research Directions

With a clearer picture of how environmental factors contribute to the Sphinx's weathering, researchers are now poised to explore future directions that could reshape our understanding of this ancient monument's age.
Through innovative studies, you'll see how collaboration among geologists, archaeologists, and historians can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
Future research may focus on:
- Advanced geological studies utilizing non-invasive techniques to analyze erosion patterns.
- Exploring climate data from prehistoric periods to understand environmental conditions influencing the Sphinx's construction.
- Applying cutting-edge technology, like 3D scanning and digital modeling, to visualize structural changes over time.
- Investigating historical records and oral traditions to uncover alternative narratives about the Sphinx's creation.
- Enhancing interdisciplinary approaches that combine scientific findings with cultural insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is the Sphinx Older Than the Egyptians?
You might find it fascinating that many researchers argue the Sphinx could be older than the Egyptians.
Geological evidence suggests it experienced significant water erosion, indicating a wetter climate long before the Egyptian civilization thrived.
This aligns with theories suggesting it dates back to around 10,000 BC or even earlier.
If these claims hold true, they challenge the traditional timeline of ancient Egypt and could reshape our understanding of early human history.
Is the Water Erosion on the Sphinx Debunked?
You might be surprised to learn that the evidence for water erosion on the Sphinx isn't debunked.
While skeptics argue that the findings are misinterpreted, geological studies show distinct patterns of water damage, suggesting a wetter climate existed long before the Sphinx's believed construction date.
This raises intriguing questions about its true age and the environmental conditions during its formation, challenging the traditional narratives surrounding ancient Egypt's timeline.
What Is the Evidence for the Age of the Sphinx?
To understand the Sphinx's age, you'll find geological studies revealing water erosion patterns that suggest it dates back to 5000 B.C.
Dr. Robert Schoch's research highlights that these patterns are consistent with a wetter climate over 12,000 years ago.
Additionally, the Sphinx's head shows less weathering than its body, implying it might've been recarved.
Historical accounts also point to its existence before Pharaoh Khafre, further complicating the dating process.
Was the Great Sphinx Built Before the Pyramids of Giza True or False?
You might wonder if the Great Sphinx was built before the Pyramids of Giza.
Evidence suggests it could be true. Geological studies show significant water erosion on the Sphinx, indicating it may have been constructed during a wetter climate, possibly long before the pyramids.
Additionally, historical figures like Sir Flinders Petrie believed the Sphinx predates the Old Kingdom, hinting at an even older timeline than what traditional Egyptology claims.
Conclusion
As you explore the Sphinx age debate, you can't help but question the established timeline of Egypt's history. With Dr. Robert Schoch's research suggesting that the Sphinx could be over 10,000 years old, you've got to contemplate the implications of such an assertion. This challenges not only our understanding of ancient civilizations but also the geological evidence of erosion. As future research unfolds, you'll find yourself captivated by the mysteries that lie beneath the sands of time.