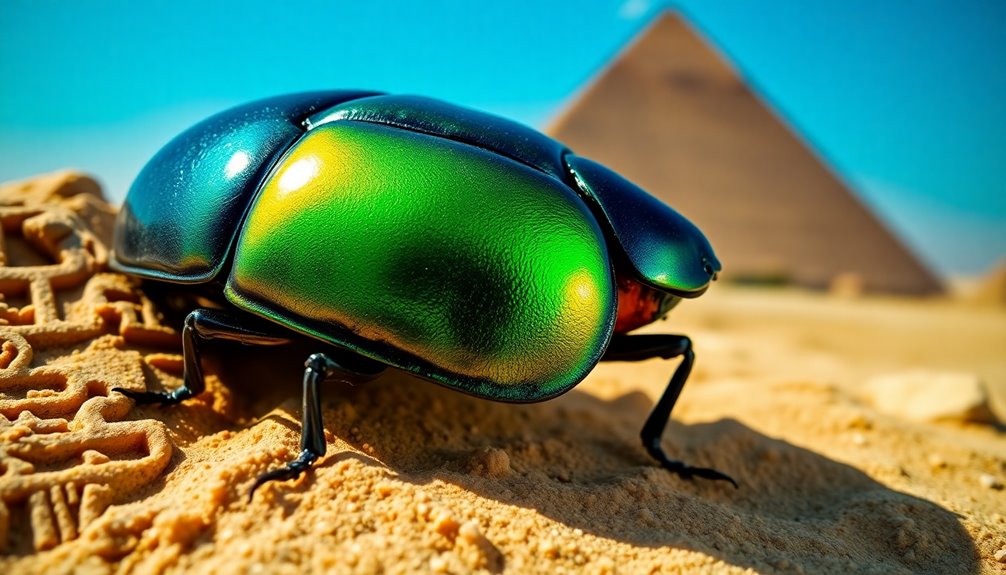
Ancient Egyptian scarab beetles are fascinating symbols of life and regeneration. You'll find them linked to the sun god Khepri, who represents rebirth. Scarab amulets were vital for protecting the deceased on their journey to the afterlife. Crafted from colorful materials like jasper and faience, these beetles weren't just decorative; they served as seals and symbols of authority. Remarkably, archaeological discoveries, including a 3,500-year-old scarab in Israel, highlight their cultural significance and ties to ancient beliefs. If you're intrigued by this rich history, there's much more to uncover about scarabs and their legacy in ancient Egypt.
Key Takeaways
- Scarabs were associated with the god Khepri, symbolizing rebirth and the daily rising of the sun in ancient Egyptian mythology.
- Scarab amulets were placed in tombs to protect the deceased and ensure safe passage into the afterlife.
- Scarabs were crafted from various materials, including steatite and faience, often inscribed with names of pharaohs for royal significance.
- Archaeological finds, including a 3,500-year-old scarab in Israel, highlight the cultural influence of ancient Egypt beyond its borders.
- Scarabs served as seals for important documents, conveying authority and marking ownership in ancient Egyptian society.
Significance in Ancient Egyptian Religion

Why did the ancient Egyptians hold the scarab beetle in such high regard? The scarab beetle was closely associated with the god Khepri, who represented the rising sun and creation. Egyptians believed Khepri rolled the morning sun disk over the horizon, symbolizing rebirth each day. This connection made the scarab a powerful symbol of renewal and regeneration, embodying life emerging from death.
You'd also notice that the beetle's behavior of rolling dung balls mirrored the life cycle, representing spontaneous self-creation. As the young hatched from these balls, it reinforced the idea of life continually rising from death, resonating deeply within the Egyptian psyche. Additionally, the scarab beetles were frequently used as amulets for protection, reflecting their significance in safeguarding the deceased.
In funerary practices, scarab amulets played a crucial role. You'd find them placed in tombs to ensure safe passage into the afterlife. Often, they were put on the heart during mummification, symbolizing its importance in the afterlife and providing protection during the final judgment.
Additionally, scarabs frequently appeared in art and hieroglyphs, emphasizing their significance in Egyptian religion. Through these associations, the scarab became a potent emblem of life, death, and the divine cycle of existence.
Roles in Ancient Egyptian Culture

In ancient Egyptian culture, the scarab beetle played a vital role beyond its religious significance. It was deeply integrated into funerary rituals, where scarab amulets were placed in tombs to ensure the deceased's safe passage into the afterlife. You'd find these amulets resting on the heart during mummification, symbolizing its importance in the journey beyond. The scarab represented the cycle of life, death, and rebirth, embodying hope for resurrection.
Scarabs also found their place in jewelry and personal adornments. You could wear scarab pendants, bracelets, or rings crafted from clay, precious gems, or metals, all designed to bring good luck and protection. The widespread use of scarabs across all social classes highlights their significance. Additionally, scarabs were often crafted from materials such as clay and precious gems, showcasing their artistic value.
In administrative contexts, scarabs served as seals for important documents, often engraved with hieroglyphics. They conveyed authority and power, marking the significance of the bearer's identity.
Moreover, scarabs appeared in various artistic forms, symbolizing life, regeneration, and transformation. Their portrayal reflected deep connections to the sun god Khepri and the cycle of daily rebirth, reinforcing their essential role in ancient Egyptian culture.
Types and Materials of Scarabs

Craftsmanship and creativity defined the types and materials of scarabs in ancient Egypt, showcasing the skilled artisans who brought these symbols of life and renewal to existence.
Scarabs were crafted from various materials, with steatite being a popular choice due to its workability. Faience, a glazed ceramic, became especially favored during the New Kingdom, while hardstones like green jasper and carnelian offered durability. Other stones such as limestone, basalt, and turquoise also played a role in scarab production.
You'd find different construction types, such as carved scarabs, which displayed intricate details of the beetle, and molded scarabs made from faience or terra-cotta. Inscribed scarabs featured hieroglyphs, serving as seals, while commemorative scarabs celebrated significant events. Sizes varied, with most falling between 10 mm and 20 mm, though larger examples existed for special occasions. Scarabs were often inscribed with names of pharaohs, reflecting their royal status in ancient Egyptian society.
Artisans used a range of tools, including flint and later copper and bronze, to shape and detail these creations. Scarabs evolved into various forms, from simple pieces to ornate jewelry, ensuring their enduring presence in ancient Egyptian culture.
Symbolism and Mythology Explained

The scarab beetle holds profound symbolism in ancient Egyptian culture, representing life, death, and rebirth. You can see its strong connection to the sun god Khepri, who embodies the rising sun and creation. The beetle's habit of rolling dung balls mirrors Khepri rolling the sun disk across the sky, symbolizing the sun's daily journey and renewal.
Additionally, the beetle's behavior signifies the cycle of life, death, and rebirth. The dung ball serves as nourishment for the larvae, illustrating regeneration and the emergence of life from death. This transformation reflects not just personal change, but societal evolution as well. Scarabs often inscribed with the names of pharaohs signify their status and beliefs, demonstrating the importance of scarabs in ancient Egyptian society.
Scarabs were also used as protective amulets and jewelry, believed to bring good fortune. Often placed in tombs, they ensured a safe passage for the deceased into the afterlife. During mummification, scarabs symbolized the heart's significance, reinforcing their role in funerary rituals.
In essence, the scarab beetle encapsulates the concepts of existence, manifestation, and divine transformation, deeply woven into the fabric of ancient Egyptian spirituality.
Archaeological and Historical Insights

Scarab beetles have played a crucial role in understanding ancient Egyptian civilization through archaeological discoveries and historical insights. You'll find these fascinating artifacts in various archaeological sites, such as tombs and burial grounds from the 1st Dynasty. A recent find of a 3,500-year-old scarab in Israel highlights how far-reaching their influence was, indicating the Egyptian presence beyond their borders. Notably, many significant finds, like the one discovered by a 12-year-old girl, reveal the extent of Egyptian cultural impact in the region. This particular scarab is adorned with the image of two scorpions that symbolize the Egyptian goddess Serket, showcasing the scarab's deep ties to ancient beliefs.
Historically, scarabs served as personal and administrative seals, often inscribed with hieroglyphs. This practice not only marked ownership but also played a role in funerary rituals, ensuring safe passage to the afterlife. Larger scarabs commemorated royal achievements, showcasing the power of figures like Amenhotep III. As you explore archaeological sites like Tel Qana, the distribution of scarabs across different regions helps illustrate Egyptian trade and diplomacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Were Scarabs Used in Daily Life by Ancient Egyptians?
In daily life, ancient Egyptians used scarabs in various ways.
You'd find them in jewelry, where they'd bring you good luck and protection. People from all walks of life wore scarab amulets to repel bad luck and safeguard against illness.
Additionally, scarabs served as seals for important documents, showcasing your authority. Their cultural significance was immense, symbolizing the cycle of life and the hope for rebirth, making them integral to daily existence.
What Was the Process of Creating Scarab Amulets?
To create scarab amulets, you'd start by selecting a raw material, like soapstone, and carve it into an oval shape.
Using finer tools, you'd add intricate details.
After smoothing the surface, you'd drill a hole for stringing.
Then, you'd apply a glaze and fire the scarab in a kiln to enhance its color.
Finally, you'd check the quality, ensuring it meets standards before it's adorned with symbols or hieroglyphs on the underside.
Did Scarabs Have Any Medicinal Uses in Ancient Egypt?
Scarabs didn't have direct medicinal uses in ancient Egypt. Instead, their significance lay in symbolism and spirituality.
You'd find scarab amulets used during mummification to protect the heart and ensure a safe passage to the afterlife. While these amulets mightn't have healed physically, they symbolized protection and well-being, influencing your mental state.
The scarab's connection to life and rebirth offered a form of spiritual comfort rather than tangible medical benefits.
How Did Scarabs Influence Ancient Egyptian Trade Practices?
Scarabs played a significant role in shaping ancient Egyptian trade practices. You'd notice how their designs spread through trade routes, influencing neighboring cultures.
Scarabs were used as luxury items and symbols of power, often exchanged in diplomatic dealings. Their presence in tombs and artifacts highlighted the extensive trade networks that connected Egypt to places like Nubia and Greece.
This exchange not only enriched local economies but also fostered cultural interactions and artistic adaptations.
Were Scarabs Associated With Any Specific Pharaohs or Dynasties?
Yes, scarabs were closely associated with specific pharaohs and dynasties.
You'll find that powerful rulers like Hatshepsut used ornate scarabs as symbols of authority.
During the New Kingdom, these beetles became prominent in funerary rituals, offering protection and ensuring safe passage to the afterlife.
Each dynasty, from the Old Kingdom to the Ptolemaic period, utilized scarabs to signify rebirth, making them essential in royal burials and cultural practices throughout ancient Egypt.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the scarab beetle isn't just an insect; it's a powerful symbol of transformation and rebirth in ancient Egyptian culture. Its significance stretches from religious practices to artistic representations, reflecting the deep beliefs of a civilization that revered nature. As you explore the various types and materials of scarabs, you'll uncover fascinating archaeological insights that reveal how this small beetle left a monumental mark on history. Embrace the wonder of scarabs and their enduring legacy!